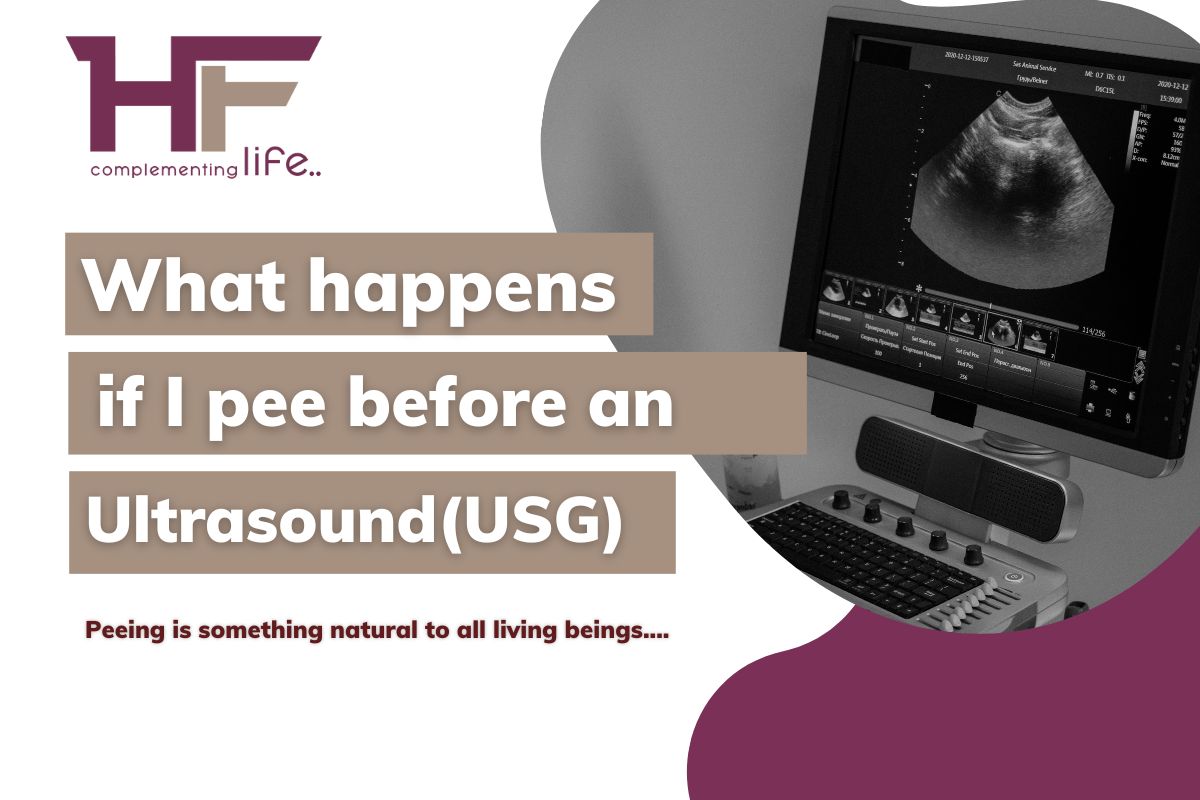
“What happens if I pee before an Ultrasound?” You, of course, can! Peeing is something natural to all living beings and expecting to not feel so at odd times is, in itself, odd!
But,
If the accuracy of an ultrasound result is what concerns you, then following the respective instruction regarding whether or not to pee before the diagnostic test stands requisite!
What did the medical professionals say? Did they ask you to pee & empty your bladder before the diagnosis? Or, did they recommend you to keep your bladder full and control your urine for some time until the test is complete?
Did they say you can pee and immediately drink 32 ounces of water to enter the ultrasound test lab?
Or, Did they say that it doesn’t matter whether you or not before the test?
Well, you shall encounter either of the above, depending on the kind of ultrasound you are going for!
Yes, ultrasound, also called ultrasonography, is not just one of the commonly practiced diagnostic methods, but also a versatile one! It means an ultrasound can serve to screen the medical conditions of a variety of organs in your body, from the reproductive organs to the urinary organs, from cardiovascular organs to respiratory organs, gastrointestinal organs, digestive organs, and so forth!
Since 1956, ultrasound, as a diagnostic technique, is going through massive growth & development, with one technique superseding the other at some point in time, in terms of its application & usage.
That’s how ultrasound became a multi-fold imaging test where the preparation varies from traditional method to the latest and from one particular internal location of examination to another!
Are you eager to note which types of ultrasound give you the opportunity to pee before entering the test lab and which ones do not? Well, that is exactly why we are here to guide you!
This article shall shed light upon the major question – What happens if you pee before an ultrasound? But, before going to that, you have to know what an ultrasound is, when you need it, what are the different types, and when peeing becomes a matter of concern for an ultrasound!
So, let us straightaway dive into the details now!
CContents
An Ultrasound Test: What is it & How does it work?
The practice of using sound waves to assess the internal organs of the human body is called ultrasound, and the practice began after the second world war at various places across the globe.
Although the idea of using ultrasound to create images was first brought into the picture by SY Sokolov, a Russian physicist, in 1928, the concept was transformed into medical practice in 1956 by Obstetrician Ian Donald & Engineer Tom Brown in Glasgow!
Since then, ultrasound tests are serving massively in medical diagnosis, particularly for obstetrics & gynecology. Today, we know how common this method is. And perhaps, the safest diagnostic process to date.
No radiation, no risk factors!
No surgery, no complications!
All it involves are – A probe or a wand-like slim instrument called a transducer, a computer console, & a video monitor. Yes, with these three pieces of equipment, a team of medical caregivers comes into action, diagnosing your internal health!
It can be a routine diagnosis that takes place at times of pregnancy or when you want a thorough body check-up.
On the other hand,
It can be a recommendation made by your doctor who predicts certain health deficits in your body and wants to confirm it via this imaging test.
Whatsoever it be, the process of diagnosis is more or less the same! Sometimes, internal, where minimal invasion takes place, and otherwise external, where no invasion takes place at all!
A radiologist, alongside an ultrasound technician or sonographer, shall conduct this test. It usually takes place at any diagnostic center, clinic, or hospital on an outpatient basis. It means for the pursuit of ultrasound, you do not need to stay in the center for long. Instead, you can leave as soon as the test is complete and go back to your normal schedule. Of course, it is because the test takes barely 15 minutes or so!
Now, you must be wondering how the process exactly works!
Let me tell you that,
- The moment you enter the test lab, you shall come across a large examination table. It is where the medical professionals shall ask you to lie down for the physical examination and expose the definite body part of the assessment.
- Once you do so, the sonographer, on the instructions of the radiologist, shall bring the transducer into play, applying a lubricant over it and/or covering it with a plastic sheet that somewhat resembles a condom.
- Then, the sonographer shall either insert the transducer through your vaginal opening or mouth or press it over your skin near the location of the examination. The lubricant applied herein shall eliminate air from the area between your skin or tissues & the transducer and allow an easy passage for the high-frequency sound waves.
- The sound waves, on traveling to different parts, shall likely hit an organ or tissue. Thereupon, reflecting back to the transducer! You will not hear them. You will not feel them. But, they shall make a faint echo. They are the electric signals that now take the stage, creating images on your computer screen.
- The radiologist sitting in front of the computer can see the inside of your body and assess the condition. He may ask you to hold on to a particular position or shift to a different one depending upon the need for images. Such a step allows him to see through your body from multiple angles.
- When the radiologist is satisfied with the images, he shall instruct the sonographer to remove the transducer and allow you to leave the test lab. You can, now, dress up as you came and wait for some time to see if any discomfort is occurring. Meanwhile, the medical professionals shall check the images and prepare them to send to your doctor.
Is that all? Yes, it is! Your physical examination stands successful, and you can go back home or to your workplace.
Reasons for Your Doctor to Recommend an Ultrasound Test!
Apart from a routine test, why will your doctor recommend an ultrasound? There must be something wrong with your health that your doctor can predict. Of course, your doctor shall recommend you to have an ultrasound and its type depending on the symptoms you have!
So, what are the symptoms you encounter these days? Do you witness –
- Persistent pelvic or abdominal pain?
- Severe Backaches?
- Fever accompanied by fatigue & nausea?
- Blood in your stools?
- Blood in your urine?
- Frequent urination at night?
- Abnormal weight loss?
- Chronic heartburn?
- Bloating?
- Tenderness near your abdomen or stomach?
- Missed periods?
- Heavy or prolonged periods?
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding or spotting?
- A burning sensation when you pee?
- Pain while having sex?
- Inability to have an orgasm?
- An unusual vaginal discharge along with an unpleasant odor?
- Urine leakage while coughing, sneezing, or laughing?
- Excessive hair growth in your chest, stomach, or back?
- Inability to conceive for long?
- Breathing problem?
- Difficulty swallowing food?
- Irritation in the breast skin?
- Swelling near the nipples?
- Change in breast size, shape, or color?
- Breast pain?
- Unusual nipple discharge?
- Rashes & Redness near your nipples?
- Constipation?
- Diarrhea?
- Pain in the anus or rectum?
- A bulge at the anus?
- Pain in the neck, throat, or jaw?
- Chronic chest pain or discomfort?
- High Blood Pressure or hypertension?
- Persistent indigestion?
Or, do you witness something more? In either of the cases, your doctor shall primarily recommend an ultrasound. It is because she predicts that you may be vulnerable to –
- Cysts, Fibroids, or Tumors,
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD),
- Urinary Tract Infections,
- Infections in your Liver, Ureter, Kidney, Pancreas, Stomach, or Bladder,
- Gallstones, Kidney Stones, or Bladder Stones,
- Pelvic organs prolapse,
- Pelvic inflammatory diseases,
- Bladder Dysfunction,
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS),
- Fatty Liver Disease,
- Enlarged Spleen,
- Liver inflammation or Hepatitis,
- Inflammation of Colon or Diverticulitis,
- Pancreatitis,
- Gastritis,
- Appendicitis
- Hernia,
- Peptic Ulcers,
- Celiac Disease,
- Narrow or thick stomach muscles,
- Collection of fluids in the abdominal cavity,
- Kidney blockage or Cancer,
- Liver Cancer,
- Breast Cancer,
- Aortic Aneurysm,
- Endometriosis,
- Ovary Torsion,
- Coronary Heart Disease,
- Peripheral Artery Disease,
- Pneumonia,
- Pulmonary Fibrosis,
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease or in short COPD,
- Bronchitis,
- Fibrocystic Breast Disease,
- Breast Lumps,
- Gynecomastia or excessive development of male breast tissue,
- Fat necrosis or injury in the breast tissues due to excess fat,
- Hemorrhoids,
- Colitis,
- Anal Fissure,
- Colon Cancer,
- Fistula,
And so forth!
Your doctor may also suggest an ultrasound during pregnancy to confirm –
- The heartbeat of the embryo inside you is normal,
- Your baby is growing,
- There is no complication like miscarriage or premature delivery,
- You are not having an ectopic pregnancy where the embryo grows right in the fallopian tube,
- Which stage of pregnancy you are in,
- Whether the abortion was successful,
- Whether the in-vitro fertilization was successful,
- Whether there is any abnormality in your placenta, and
- The source of your abnormal vaginal bleeding.
In fact, doctors ask for an ultrasound to see how well is the intrauterine devices placed!
Now that you know the different medical conditions ultrasound can trace, you must be keen to know which type of ultrasound traces what. Read below to learn the various ultrasound methods!
Outlining the Different Types of Ultrasound Tests!
Well, traditional ultrasound is classified according to the location of the examination. It means the doctor, on hearing your symptoms, shall understand where the abnormality situates within your body and accordingly suggest the type of ultrasound. The different types of traditional ultrasound are as follows!
- Pelvic ultrasound – This is the ultrasound process, diagnosing your pelvic organs like ureter, uterus, fallopian tube, urinary bladder, urinary tract, rectum, placenta, etc. This type of diagnostic ultrasound can be further divided into three types, namely, – abdominal ultrasound, vaginal ultrasound, & rectum ultrasound. While the former is an external method that requires no invasion, the latter two undergo minimal invasion, and they are internal processes.
- Breast ultrasound – This ultrasound method involves the diagnosis of your breasts & helps healthcare providers find defects in your breast tissues and those of the nearby areas. Thy be a painless procedure, entailing no invasion at all. Taking the stage in 1970, this method today is indispensable to medical science. It is rapid & cost-effective!
- Carotid ultrasound – A carotid ultrasound shows the condition of your carotid arteries, especially when they turn narrow due to a build-up of plaque, increasing the risk of stroke. In fact, this particular method also lay used to detect cerebrovascular diseases, like thrombosis, stenosis, hemorrhage, & embolisms, or blockages. It is typically a non-invasive method and therefore does not encompass any pain or discomfort.
- Thyroid ultrasound – Another significant ultrasound test is the thyroid ultrasound. In this process, your healthcare providers can screen the condition of your thyroid glands. Your doctor shall recommend this test when a thyroid function test fails to assess the abnormality. It is sometimes used as a routine test to detect overactive or underactive thyroid, and sometimes to detect whether you have lumps or a large goiter in your thyroid gland. It is a minimally-invasive procedure where the transducer is inserted through your mouth. And hence called an internal ultrasound.
- Musculoskeletal ultrasound – It is the type of ultrasound where the medical caregivers examine your muscles, joints, tendons, ligaments, nerves, and others. A dynamic process thy be, allocating dynamic images, even of the superficial musculoskeletal structures! It is fast, safe, and cost-effective and diagnoses the muscles existing throughout your body. Musculoskeletal ultrasound is an external, non-invasive procedure encompassing a linear transducer.
Wait! That is not all!
Apart from the traditional ultrasound methods, there exist some others! They are the latest developments of medical science to bring forth precision & dexterity to the process of ultrasound and are as follows.
- Doppler Ultrasound – Doppler Ultrasound is an advanced method of ultrasound that comes into the picture when traditional ultrasound fails to capture the imaging of blood flow in the arteries & veins. In this process, the sound waves, on encountering & bouncing off moving objects like the Red Blood Cells, streamline images on the computer screen. Invented by Dennis Watkins, Don Baker, & John Reid, the Doppler Ultrasound technology serves to assess blood flow throughout the different layers of your heart.
- Color Doppler Ultrasound – A color doppler ultrasound is a further modified process of ultrasound testing where just like the former, the bloodstream throughout your body across the many layers gets assessed. The only modification done herein is the coloring of the images. In other words, a color doppler ultrasound shall offer you colored images after the test, subsequently, ensuring better visibility by highlighting the direction of blood flow.
- Duplex Ultrasound – The third and most significant diagnostic approach of an ultrasound is the Duplex one! Herein, the sound waves aim to produce two-dimensional imaging of your organs & tissues. It serves mostly in revealing conditions like blockages or prolapse. The special interpretation that it offers helps the doctor accurately conduct therapies. This process involves the use of two transducers, one called Doppler and the other B-mode.
- Triplex Ultrasound – Just like the above, triplex ultrasound is a further modification technique where three-dimensional imaging comes into existence after the diagnosis stands complete! This particular modification was done to acquire a profound visualization of the blood flow to your internal organs and can scan peripheral vasculatures.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound – Then comes a twin-fold diagnostic approach of ultrasound where the ultrasound technique is combined with the endoscopic techniques to culminate better results. In other words, the transducer works alongside an endoscope to create systematic images of your internal organs. Such a method is mostly used to diagnose and simultaneously treat digestive diseases, like pancreatic lesions, gastrointestinal tract infections, etc. Alas! This particular method may not be totally free from side effects or complications as ionizing radiations are involved in the process of diagnosis!
- Saline Infusion Sonography – Above all, there exists a more latest ultrasound approach, comprising the intervention of salt solution or saline to create 100 percent sensitivity in the diagnostic process. The saltwater helps screen your internal organs with greater dexterity & precision, confirming medical conditions like endometriosis or endometrial cavity. This method has become a popular diagnostic approach in recent times for uterine pathology & tubal patency.
Medical research is going on to bring up further modifications in ultrasound technologies, but these are the standard methods followed today and yet differ from each other in their preparation.
By now, we all know that peeing before an ultrasound is a matter of concern before up-taking an ultrasound. But how exactly?
Let us discover it down the line!
In an Ultrasound: When Does Peeing Become a Matter of Concern?
Peeing becomes a matter of concern before an ultrasound and is precisely why doctors provide instructions on whether or not to release your urine before the diagnostic test. Not just for ultrasound, in particular, all diagnostic tests hold the concern of peeing to cultivate accurate test results.
Especially when it comes to the assessment of pelvic or abdominal organs, your urine which is likely to appear dark grey or black on the ultrasound screen becomes a significant marker. It is because when sound waves travel through your body, they come across different mediums, like fluids, air, and so forth. In this context, the reservoir of fluids can sometimes act as an enhancement to the movement of sound waves and sometimes just the opposite.
Therefore, the medical caregivers, for extracting a clear view of the body structure, instructs whether to release your urine or keep the fluids intact within your body!
However, it isn’t a matter of concern for ultrasound types like breast ultrasound, musculoskeletal ultrasound, or thyroid ultrasound, but matters for the pelvic categories, such as vaginal ultrasound, abdominal ultrasound, and rectal ultrasound.
While in the case of abdominal ultrasound & rectal ultrasound, a full bladder stands necessary, in the case of vaginal ultrasound, you need to keep your bladder empty. Why so? Simply because the ultrasound technique for an abdominal or rectal one shall work to assess the volume of your bladder, for which you need to keep control of the urine and avoid it leaking until the ultrasound is over! Also, it is important to note, in this regard, that a full bladder pushes your bowel out of the pelvis, thereby permitting the transmission of sound waves to the target organs in your body.
On the other note, the vaginal ultrasound seeks to diagnose your organs with an empty bladder because, in this minimally-invasive procedure, there is a possibility for your uterus to undergo distortion. An empty bladder shall limit this possibility, which is common when your bladder stands full! Besides, an empty bladder in case of vaginal ultrasound can reduce your discomfort & simultaneously refrains urinary tract infection that may arise from the situation of contact between the transducer & your urinary waste inside your body. And same goes for an endoscopic ultrasound technique!
Yet again, for an early pregnancy ultrasound, a full bladder stands requisite. It is because until 24 weeks of pregnancy, the amount of amniotic fluid in your body lay insufficient, and your doctor has to compensate for that with something to get clarity in the test result. So, what is the solution? The natural one that you already have – Urine!
Last Words from HealthFinder:
Hey, did you get your answer to the question you were looking for? If so, you can now go ahead with the definite ultrasound process you are recommended. And if not, you can share your doubt with us at www.healthfinder.in. Our team of caregivers shall reach out to you at its earliest.
And,
If you want to know more about the preparation before an ultrasound, keep reading our blogs and keep checking our website. You can get all medical information on our website with just a few clicks.
Thank you for stopping by! Thank you for hearing out!




Comments